Welcome to Our Company
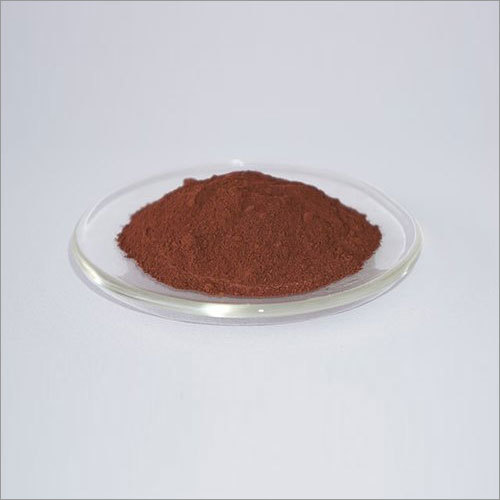
Palladium Chloride
3650 INR/Gram
Product Details:
- CAS No 7647-10-1
- Application Industrial
- Physical Form Powder
- Molecular Formula PdCl2
- Density 4 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Melting Point 679 C
- Storage Room Temperature
- Click to View more
X
Palladium Chloride Price and Quantity
- 10 Gram
- 3650 INR/Gram
Palladium Chloride Product Specification
- Technical Grade
- 12 Months
- 231-596-2
- 177.33 GSM (gm/2)
- 99%
- Water
- 679 C
- 4 Gram per cubic centimeter(g/cm3)
- Room Temperature
- 7647-10-1
- PdCl2
- Powder
- Industrial
Product Description
Available in free flow powder form, Palladium Chloride is used as an important part of Wacker process that involves oxidation of ethylene. This specific process is executed to produce acetaldehyde in presence of Palladium Chloride. This powder based chemical is also effective in removal of stubborn stain marks from stainless steel surface and also to verify corrosion resistance capacity of metal. Offered chemical easily dissolves in water based form of metal halides, organic solvents, cold water and also in hydrochloric acid.
Palladium Chloride Properties:
1. Chemical Formula: PdCl2
2. Molar Mass: Approximately 177.33 g/mol
3. Appearance: Palladium chloride typically appears as a dark brown or black solid at room temperature.
4. Melting Point: The melting point of PdCl2 is around 551 degree centigrade.
5. Boiling Point: The compound does not have a well-defined boiling point, as it decomposes at high temperatures.
6. Solubility: Palladium chloride is soluble in water and various organic solvents, including ethanol, methanol, and acetone.
7. Hygroscopicity: It has some degree of hygroscopicity, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air.
8. Redox Chemistry: Palladium chloride can participate in various redox reactions, interconverting between different oxidation states of palladium.
9. Ligand Exchange: The compound can undergo ligand exchange reactions, where the chloride ions can be replaced by other ligands, leading to the formation of different palladium complexes.
Uses of Palladium Chloride:
Palladium chloride (PdCl2) and its derivatives have various important uses in different fields. Some of the primary applications of palladium chloride include:
1. Catalysis: Palladium chloride is widely used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. It is particularly valuable in various cross-coupling reactions, such as the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling, Heck reaction, and Sonogashira coupling. These reactions are essential in the synthesis of complex organic molecules and pharmaceuticals.
2. Electroplating: Palladium chloride is utilized in electroplating processes to deposit a thin layer of palladium metal onto the surface of other materials. Palladium-plated materials have excellent corrosion resistance and are often used in electronics, jewelry, and certain industrial applications.
3. Hydrogenation: Palladium chloride is used as a catalyst in hydrogenation reactions, where hydrogen gas is added to unsaturated compounds to convert them into saturated compounds. This process is widely employed in the production of various industrial chemicals and pharmaceutical intermediates.
4. Organic Transformations: Palladium chloride is involved in a range of organic transformations, including oxidation and reduction reactions. It can mediate the conversion of alcohols to aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids and facilitate the reduction of carbonyl compounds to alcohols.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry: Palladium-catalyzed reactions play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry for the synthesis of drug candidates and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The use of palladium catalysis often enables more efficient and environmentally friendly synthetic routes.
6. Analytical Chemistry: Palladium chloride is utilized as a reagent in certain analytical chemistry procedures, particularly in the determination of trace amounts of various elements.
7. Palladium-Based Medicines: Some palladium complexes are being investigated for potential medical applications, including cancer treatment. These compounds have shown promising anticancer activity in preclinical studies.
8. Fine Chemicals and Specialty Materials: Palladium chloride is used in the production of fine chemicals and specialty materials, including high-purity palladium metal and palladium compounds.
FAQ:
Q. What is palladium chloride, and what is its chemical formula?
Ans: Palladium chloride (PdCl2) is a chemical compound composed of palladium and chlorine.
Q. What does palladium chloride look like?
Ans: Palladium chloride typically appears as a dark brown or black solid at room temperature.
Q. What are the main uses of palladium chloride?
Ans: Palladium chloride is primarily used as a catalyst in various organic synthesis reactions, electroplating processes, and hydrogenation reactions. It also finds applications in the pharmaceutical industry, analytical chemistry, and in the development of specialty materials.
Q. How is palladium chloride used as a catalyst?
Ans: Palladium chloride serves as a catalyst in many organic reactions, facilitating the formation or breaking of chemical bonds in the reactants without being consumed in the process. It is particularly valuable in cross-coupling reactions, such as the Suzuki-Miyaura and Heck reactions.
Q. Can palladium chloride be used for electroplating?
Ans: Yes, palladium chloride is commonly used in electroplating processes to deposit a thin layer of palladium metal onto the surface of other materials. Palladium-plated materials are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and are used in electronics and jewelry, among other applications.
Q. Is palladium chloride toxic?
Ans: Palladium chloride is considered to be a hazardous substance. While it is not as toxic as some other palladium compounds, appropriate safety precautions should be taken when handling it to avoid exposure.
Q. Are there any medical applications of palladium chloride?
Ans: Some palladium compounds are being investigated for potential medical applications, particularly in cancer treatment. These compounds have shown promising anticancer activity in preclinical studies.
Q. How does palladium chloride contribute to sustainable chemistry?
Ans: Palladium chloride is used as a catalyst in many reactions that promote more efficient and environmentally friendly synthetic routes. It enables the development of green chemistry processes, reducing waste and energy consumption.
Q. What is the melting point of palladium chloride?
Ans: The melting point of palladium chloride is around 551 degree centigrade.
Q. Can palladium chloride be used in analytical chemistry?
Ans: Yes, palladium chloride is used as a reagent in certain analytical chemistry procedures, particularly in the determination of trace amounts of various elements.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email